Definition
Define an interface for creating an object, but let subclasses decide which class to instantiate. The Factory method lets a class defer instantiation it uses to subclasses
Advantages
- Good Encapsulation: The called only need to care about the class name, which helps to decouple interdependence.
- Good Expandability: Product class can be easily added by modifying or extending subclasses.
- Hide products Details:Callers and product classes are communicating by interfaces. The change of class implementation will not affect how to use these classes.
- Obey SOLID principle:
Simple Factory Pattern(Static Factory Pattern)
In simple factory pattern, we have a factory class which has a method that returns different types of object based on given input
public abstract class BMW
{
public string CarName { get; set; }
}
public class BMW320 : BMW
{
public BMW320()
{
this.CarName = "BMW320";
}
}
public class BMW532 : BMW
{
public BMW532()
{
this.CarName = "BMW532";
}
}
public class SimpleFactoryPattern
{
public BMW createBMW(int type)
{
switch (type)
{
case 3:
return new BMW320();
case 5:
return new BMW532();
default:
return new BMW320();
}
}
public static void Main()
{
var factory = new SimpleFactoryPattern();
var bmw3 = factory.createBMW(3);
var bmw5 = factory.createBMW(5);
}
}
- Simple Factory Pattern Issues
- Simple factory pattern violates Open Close Principle of SOLID principles. If we need to add another subclass, we have to change the function in factory class.
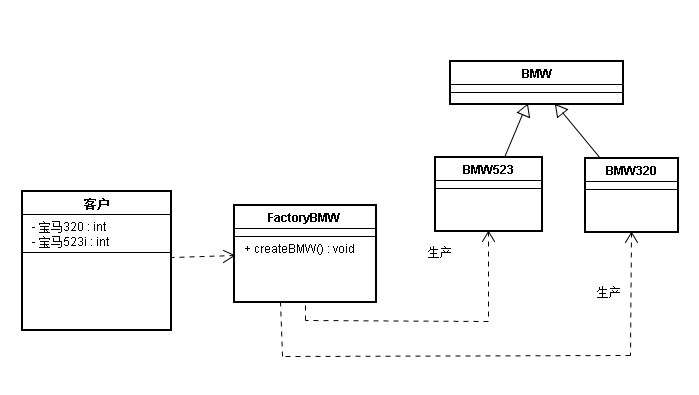
Factory Method Pattern
The factory method pattern is a design pattern that allows for the creation of objects without specifying the type of object that is to be created in code. A factory class contains a method that allows determination of the created type at run-time.
-
Components:
- Abstract Factory Class: Base class of Concrete Factory Class。
- Concrete Factory Class:Concrete factory class, which contains the detailed logical related code. It is responsible for creating concrete product objects.
- Abstract Product Class:Base class of Concrete Product Class。
- Concrete Product Class:Concrete product class, which is created by Concrete Factory Class.

public abstract class BMW
{
public string CarName { get; set; }
}
public class BMW320 : BMW
{
public BMW320()
{
this.CarName = "BMW320";
}
}
public class BMW532 : BMW
{
public BMW532()
{
this.CarName = "BMW532";
}
}
public interface FactoryBMW
{
BMW CreateBMW();
}
public class FactoryBMW320 : FactoryBMW
{
public BMW CreateBMW()
{
return new BMW320();
}
}
public class FactoryBMW532 : FactoryBMW
{
public BMW CreateBMW()
{
return new BMW532();
}
}
public class FactoryMethodPattern
{
public static void Main()
{
var factoryBMW320 = new FactoryBMW320();
var bmw3 = factoryBMW320.CreateBMW();
var factoryBMW532= new FactoryBMW532();
var bmw5 = factoryBMW532.CreateBMW();
}
}
Advantage of Factory Method Pattern
- Follows Open Close Principle. When new requirement came, just need to create an additional Factory.
Abstract Factory Pattern
The abstract factory pattern is a design pattern that allows for the creation of groups of related objects without the requirement of specifying the exact concrete classes that will be used. One of a number of factory classes generates the object sets.
-
Abstract Factory Pattern VS Factory Method/Simple Factory Pattern
- Abstract Factory Pattern: It provides different kind of Factories, each provide a particular kind of related objects.
- Factory Method/Simple Factory Pattern: It provides one kind on objects only.
-
Components:
- Abstract Factory Class: Base class of Concrete Factory Class。
- Concrete Factory Class:Concrete factory class, which contains the detailed logical related code. It is responsible for creating concrete product objects.
- Abstract Product Class:Base class of Concrete Product Class。
- Concrete Product Class:Concrete product class, which is created by Concrete Factory Class.

public abstract class BMW
{
public string CarName { get; set; }
}
public class BMW320 : BMW
{
public BMW320()
{
this.CarName = "BMW320";
}
}
public class BMW532 : BMW
{
public BMW532()
{
this.CarName = "BMW532";
}
}
public abstract class aircondition
{
public string ConditionName { get; set; }
}
public class AirConditionBMW320 : aircondition
{
public AirConditionBMW320()
{
this.ConditionName = "BMW320 AC";
}
}
public class AirConditionBMW532 : aircondition
{
public AirConditionBMW532()
{
this.ConditionName = "BMW532 AC";
}
}
public interface FactoryBMW
{
BMW createBMW();
aircondition createAirC();
}
public class FactoryBMW320 : FactoryBMW
{
public BMW createBMW()
{
return new BMW320();
}
public aircondition createAirC()
{
return new AirConditionBMW320();
}
}
public class FactoryBMW523 : FactoryBMW
{
public BMW createBMW()
{
return new BMW532();
}
public aircondition createAirC()
{
return new AirConditionBMW532();
}
public static void Main()
{
var factoryBMW320 = new FactoryBMW320();
var bmw320 = factoryBMW320.createBMW();
var bmw320Ac = factoryBMW320.createAirC();
}
}
- Disadvantages:
If we change the interface provide by Abstract Factory itself, all factories need to change.
Reference.
Design Patterns 1 of 3 - Creational Design Patterns - CodeProject
Factory Patterns - Abstract Factory Pattern - CodeProject