UICollectionView和相关类的设置非常灵活和强大。但是灵活性一旦增强,某种程度上也增加了其复杂性: UICollectionView比老式的 UITableView
更有深度,适用性也更强。
Collection View 深入太多了,事实上,Ole Begeman 和 Ash Furrow 之前曾在 objc.io 上发表过 自定义 Collection View 布局 和 UICollectionView + UIKit 力学,但是我依然有一些他们没有提及的内容可以写。在这篇文章中,我假设你已经非常熟悉 UICollectionView的基本布局,并且至少阅读了苹果精彩的编程指南以及 Ole 之前的文章。
本文的第一部分将集中讨论并举例说明如何用不同的类和方法来共同帮助实现一些常见的 UICollectionView动画。在第二部分,我们将看一下带有 collection views 的 view controller 转场动画以及在 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions可用时使用其进行转场,如果不可用时,我们会实现一个自定义转场动画。
你可以在 GitHub 中找到本文提到的两个示例工程:
布局动画
自定义 collection view 转场动画
Collection View 布局动画
标准 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 除了动画是非常容易自定义的,苹果选择了一种安全的途径去实现一个简单的淡入淡出动画作为所有布局的默认动画。如果你想实现自定义动画,最好的办法是子类化 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 并且在适当的地方实现你的动画。让我们通过一些例子来了解 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 子类中的一些方法如何协助完成自定义动画。
插入删除元素
一般来说,我们对布局属性从初始状态到结束状态进行线性插值来计算 collection view 的动画参数。然而,新插入或者删除的元素并没有最初或最终状态来进行插值。要计算这样的 cells 的动画,collection view 将通过 initialLayoutAttributesForAppearingItemAtIndexPath: 以及 finalLayoutAttributesForDisappearingItemAtIndexPath: 方法来询问其布局对象,以获取最初的和最后的属性。苹果默认的实现中,对于特定的某个 indexPath,返回的是它的通常的位置,但 alpha 值为 0.0,这就产生了一个淡入或淡出动画。如果你想要更漂亮的效果,比如你的新的 cells 从屏幕底部发射并且旋转飞到对应位置,你可以如下实现这样的布局子类:
- (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes*)initialLayoutAttributesForAppearingItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)itemIndexPath
{
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attr = [self layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:itemIndexPath];
attr.transform = CGAffineTransformRotate(CGAffineTransformMakeScale(0.2, 0.2), M_PI);
attr.center = CGPointMake(CGRectGetMidX(self.collectionView.bounds), CGRectGetMaxY(self.collectionView.bounds));
return attr;
}
结果如下:

对应的 finalLayoutAttributesForDisappearingItemAtIndexPath:
方法中,除了设定了不同的 transform 以外,其他都很相似。
响应设备旋转
设备方向变化通常会导致 collection view 的 bounds 变化。如果通过 shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange: 判定为布局需要被无效化并重新计算的时候,布局对象会被询问以提供新的布局。UICollectionViewFlowLayout 的默认实现正确地处理了这个情况,但是如果你子类化 UICollectionViewLayout 的话,你需要在边界变化时返回 YES:
- (BOOL)shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange:(CGRect)newBounds
{
CGRect oldBounds = self.collectionView.bounds;
if (!CGSizeEqualToSize(oldBounds.size, newBounds.size)) {
return YES;
}
return NO;
}
在 bounds 变化的动画中,collection view 表现得像当前显示的元素被移除然后又在新的 bounds 中被被重新插入,这会对每个 IndexPath 产生一系列的 finalLayoutAttributesForDisappearingItemAtIndexPath:
和 initialLayoutAttributesForAppearingItemAtIndexPath:
的调用。
如果你在插入和删除的时候加入了非常炫的动画,现在你应该看看为何苹果明智的使用简单的淡入淡出动画作为默认效果:
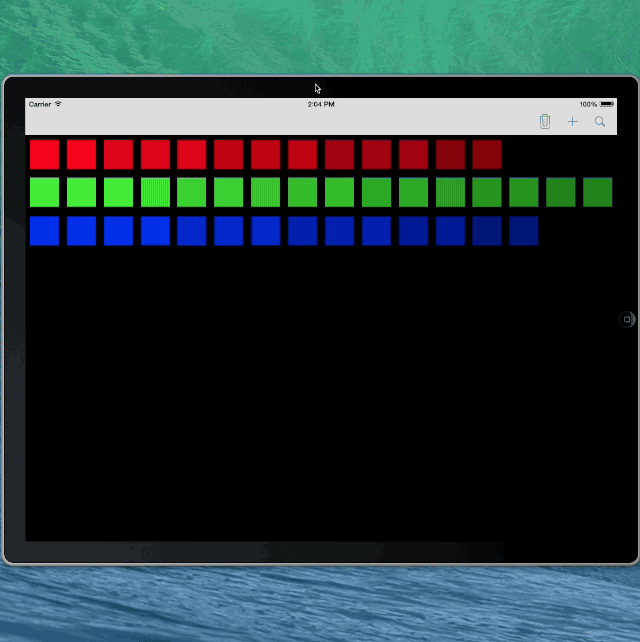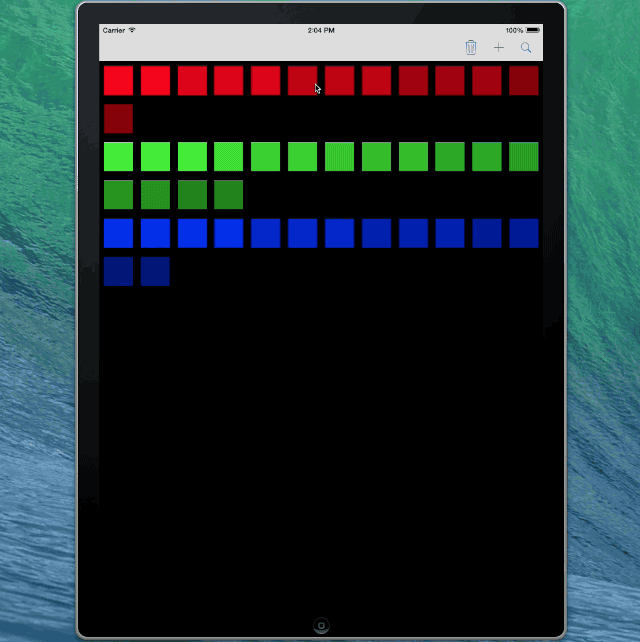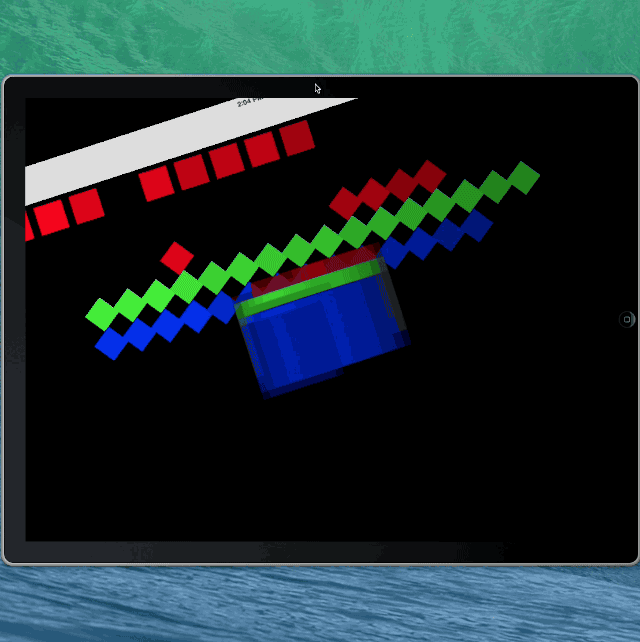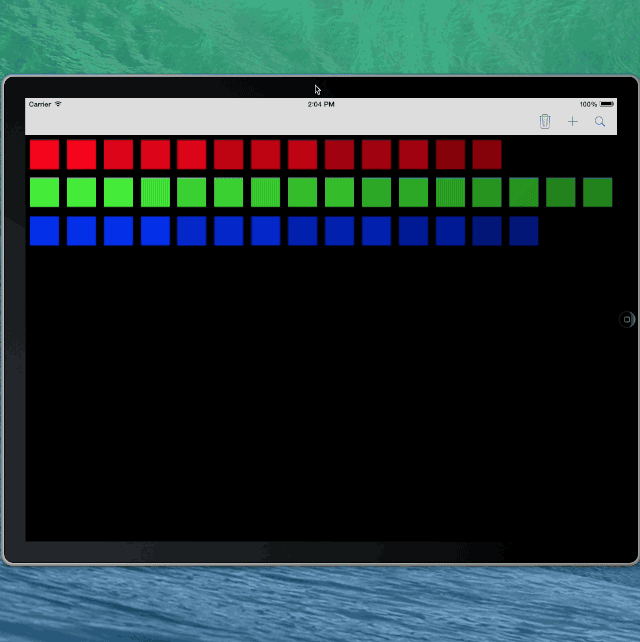
啊哦...
为了防止这种不想要的动画,初始化位置 -> 删除动画 -> 插入动画 -> 最终位置的顺序必须完全匹配 collection view 的每一项,以便最终呈现出一个平滑动画。换句话说,finalLayoutAttributesForDisappearingItemAtIndexPath:
以及 initialLayoutAttributesForAppearingItemAtIndexPath:
应该针对元素到底是真的在显示或者消失,还是 collection view 正在经历的边界改变动画的不同情况,做出不同反应,并返回不同的布局属性。
幸运的是,collection view 会告知布局对象哪一种动画将被执行。它分别通过调用 prepareForAnimatedBoundsChange:
和 prepareForCollectionViewUpdates:
来对应 bounds 变化以及元素更新。出于本实例的说明目的,我们可以使用 prepareForCollectionViewUpdates:
来跟踪更新对象:
- (void)prepareForCollectionViewUpdates:(NSArray *)updateItems
{
[super prepareForCollectionViewUpdates:updateItems];
NSMutableArray *indexPaths = [NSMutableArray array];
for (UICollectionViewUpdateItem *updateItem in updateItems) {
switch (updateItem.updateAction) {
case UICollectionUpdateActionInsert:
[indexPaths addObject:updateItem.indexPathAfterUpdate];
break;
case UICollectionUpdateActionDelete:
[indexPaths addObject:updateItem.indexPathBeforeUpdate];
break;
case UICollectionUpdateActionMove:
[indexPaths addObject:updateItem.indexPathBeforeUpdate];
[indexPaths addObject:updateItem.indexPathAfterUpdate];
break;
default:
NSLog(@"unhandled case: %@", updateItem);
break;
}
}
self.indexPathsToAnimate = indexPaths;
}
以及修改我们元素的插入动画,让元素只在其正在被插入 collection view 时进行发射:
- (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes*)initialLayoutAttributesForAppearingItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)itemIndexPath
{
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attr = [self layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:itemIndexPath];
if ([_indexPathsToAnimate containsObject:itemIndexPath]) {
attr.transform = CGAffineTransformRotate(CGAffineTransformMakeScale(0.2, 0.2), M_PI);
attr.center = CGPointMake(CGRectGetMidX(self.collectionView.bounds), CGRectGetMaxY(self.collectionView.bounds));
[_indexPathsToAnimate removeObject:itemIndexPath];
}
return attr;
}
如果这个元素没有正在被插入,那么将通过 layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath
来返回一个普通的属性,以此取消特殊的外观动画。结合 finalLayoutAttributesForDisappearingItemAtIndexPath:
中相应的逻辑,最终将会使元素能够在 bounds 变化时,从初始位置到最终位置以很流畅的动画形式实现,从而建立一个简单但很酷的动画效果:
交互式布局动画
Collection views 让用户通过手势实现与布局交互这件事变得很容易。如苹果建议的那样,为 collection view 布局添加交互的途径一般会遵循以下步骤:
- 创建手势识别
- 将手势识别添加给 collection view
- 通过手势来驱动布局动画
让我们来看看我们如何可以建立一些用户可缩放捏合的元素,以及一旦用户释放他们的捏合手势元素返回到原始大小。
我们的处理方式可能会是这样:
- (void)handlePinch:(UIPinchGestureRecognizer *)sender {
if ([sender numberOfTouches] != 2)
return;
if (sender.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan ||
sender.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateChanged) {
// 获取捏合的点
CGPoint p1 = [sender locationOfTouch:0 inView:[self collectionView]];
CGPoint p2 = [sender locationOfTouch:1 inView:[self collectionView]];
// 计算扩展距离
CGFloat xd = p1.x - p2.x;
CGFloat yd = p1.y - p2.y;
CGFloat distance = sqrt(xd*xd + yd*yd);
// 更新自定义布局参数以及无效化
FJAnimatedFlowLayout* layout = (FJAnimatedFlowLayout*)[[self collectionView] collectionViewLayout];
NSIndexPath *pinchedItem = [self.collectionView indexPathForItemAtPoint:CGPointMake(0.5*(p1.x+p2.x), 0.5*(p1.y+p2.y))];
[layout resizeItemAtIndexPath:pinchedItem withPinchDistance:distance];
[layout invalidateLayout];
}
else if (sender.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateCancelled ||
sender.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded){
FJAnimatedFlowLayout* layout = (FJAnimatedFlowLayout*)[[self collectionView] collectionViewLayout];
[self.collectionView
performBatchUpdates:^{
[layout resetPinchedItem];
}
completion:nil];
}
}
这个捏合操作需要计算捏合距离并找出被捏合的元素,并且在用户捏合的时候通知布局以实现自身更新。当捏合手势结束的时候,布局会做一个批量更新动画返回原始尺寸。
另一方面,我们的布局始终在跟踪捏合的元素以及期望尺寸,并在需要的时候提供正确的属性:
- (NSArray*)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect
{
NSArray *attrs = [super layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:rect];
if (_pinchedItem) {
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attr = [[attrs filteredArrayUsingPredicate:[NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"indexPath == %@", _pinchedItem]] firstObject];
attr.size = _pinchedItemSize;
attr.zIndex = 100;
}
return attrs;
}
小结
我们通过一些例子来说明了如何在 collection view 布局中创建自定义动画。虽然 UICollectionViewFlowLayout
并不直接允许定制动画,但是苹果工程师提供了清晰的架构让你可以子类化并实现各种自定义行为。从本质来说,在你的 UICollectionViewLayout
子类中正确地响应以下信号,并对那些要求返回 UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes
的方法返回合适的属性,那么实现自定义布局和动画的唯一约束就是你的想象力:
- prepareLayout
- prepareForCollectionViewUpdates:
- finalizeCollectionViewUpdates
- prepareForAnimatedBoundsChange:
- finalizeAnimatedBoundsChange
- shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange:
更引人入胜的动画可以结合像在 objc.io 话题 #5 中 UIKit 力学这样的技术来实现。
带有 Collection views 的 View controller 转场
就如 Chris 之前在 objc.io 的文章中所说的那样,iOS 7 中的一个重大更新是自定义 view controller 转场动画。与自定义转场动画相呼应,苹果也在 UICollectionViewController
添加了 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions
标记来在可复用的单个 collection view 间启用导航转场。苹果自己的照片和日历应用就是这类转场动画的非常好的代表作。
UICollectionViewController 实例之间的转场动画
让我们来看看我们如何能够利用上一节相同的示例项目达到类似的效果:
为了使布局到布局的转场动画工作,navigation controller 的 root view controller 必须是一个 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions设置为 NO的 collection view controller。
当另一个 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions设置为 YES的 UICollectionViewController实例被 push 到根视图控制器之上时,navigation controller 会用布局转场动画来代替标准的 push 转场动画。这里要注意一个重要的细节,根视图控制器的 collection view 实例被回收用于在导航栈上 push 进来的 collection 控制器中,如果你试图在 viewDidLoad
之类的方法中中设置 collection view 属性, 它们将不会有任何反应,你也不会收到任何警告。
这个行为可能最常见的陷阱是期望回收的 collection view 根据顶层的 collection 视图控制器来更新数据源和委托。它当然不会这样:根 collection 视图控制器会保持数据源和委托,除非我们做点什么。
解决此问题的方法是实现 navigation controller 的委托方法,并根据导航堆栈顶部的当前视图控制器的需要正确设置 collection view 的数据源和委托。在我们简单的例子中,这可以通过以下方式实现:
- (void)navigationController:(UINavigationController *)navigationController didShowViewController:(UIViewController *)viewController animated:(BOOL)animated
{
if ([viewController isKindOfClass:[FJDetailViewController class]]) {
FJDetailViewController *dvc = (FJDetailViewController*)viewController;
dvc.collectionView.dataSource = dvc;
dvc.collectionView.delegate = dvc;
[dvc.collectionView scrollToItemAtIndexPath:[NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:_selectedItem inSection:0] atScrollPosition:UICollectionViewScrollPositionCenteredVertically animated:NO];
}
else if (viewController == self){
self.collectionView.dataSource = self;
self.collectionView.delegate = self;
}
}
当详细页面的 collection view 被推入导航栈时,我们重新设置 collection view 的数据源到详细视图控制器,确保只有被选择的 cell 颜色显示在详细页面的 collection view 中。如果我们不打算这样做,布局依然可以正确过渡,但是collection 将显示所有的 cells。在实际应用中,detail 的数据源通常负责在转场动画过程中显示更详细的数据。
用于常规转换的 Collection View 布局动画
使用了 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions
的布局和布局间导航转换是很有用的,但却局限于仅在 两个 view controller 都是 UICollectionViewController
的实例,并且转场的必须发生在顶级 collection views 之间。为了达到在任意视图控制器的任意 collection view 之间都能实现相似的过渡,我们需要自定义一个 view collection 的转场动画。
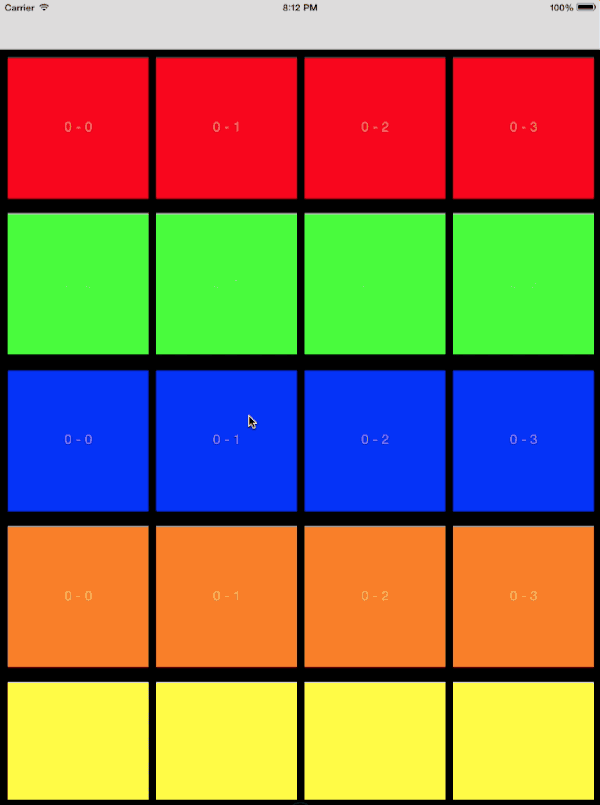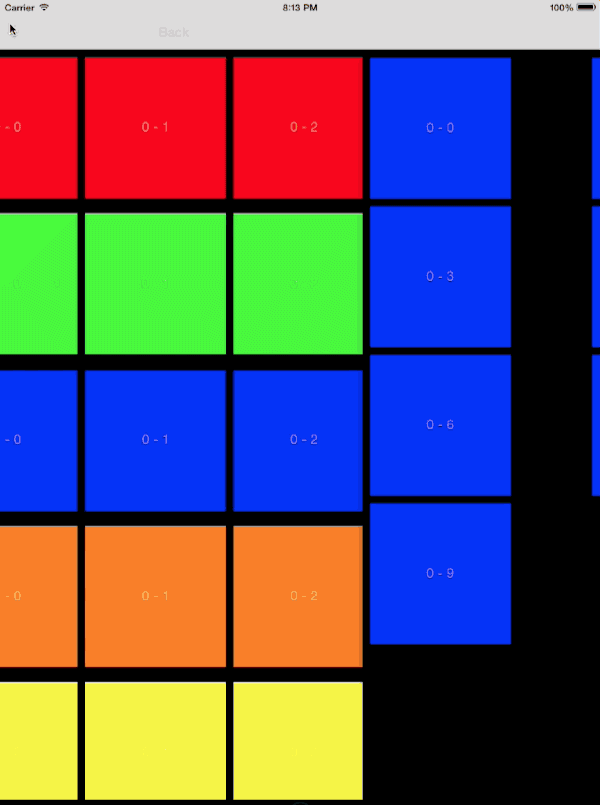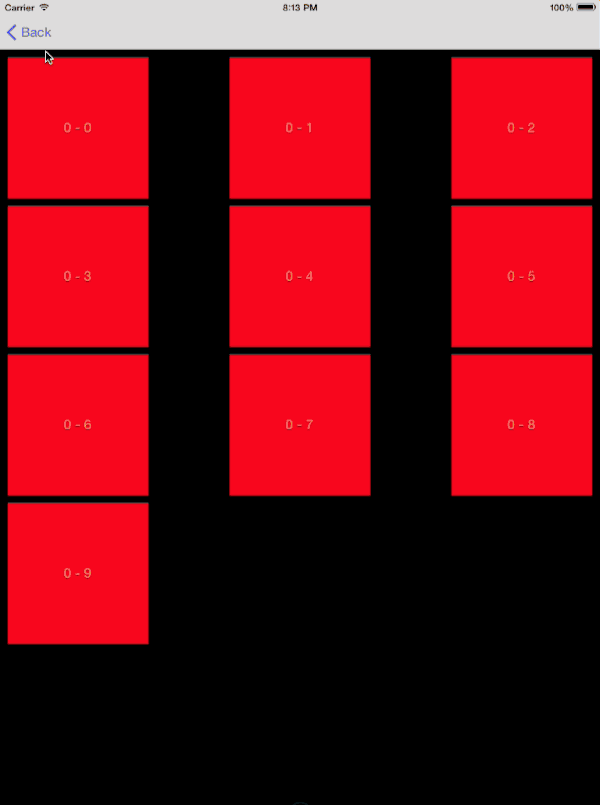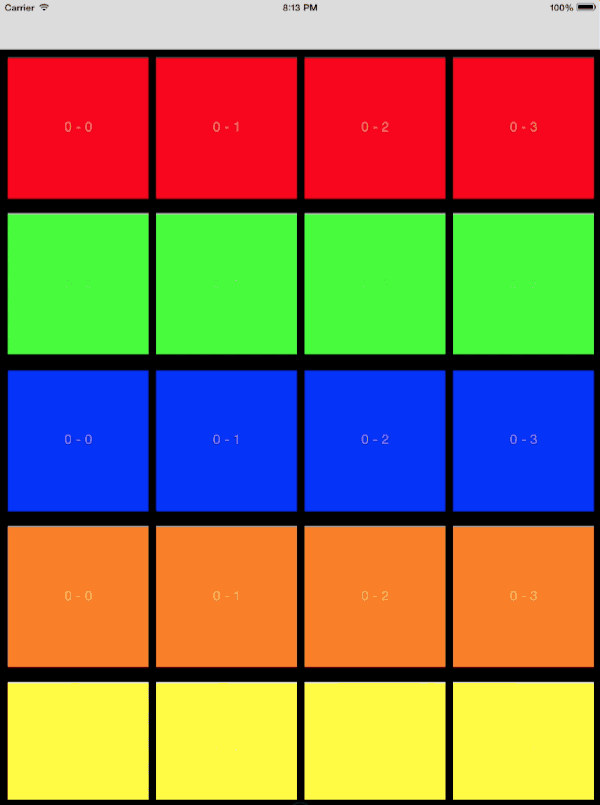
针对此类自定义过渡的动画控制器,需要遵循以下步骤进行设计:
- 对初始的 collection view 中的所有可见元素制作截图
- 将截图添加到转场上下文的 container view 中
- 运用目标 collection view 的布局计算最终位置
- 制作动画使快照到正确的位置
- 当目标 collection view 可见时删除截图
一个这样的动画设计有两重缺陷:它只能对初始的 collection view 的可见元素制作动画,因为快照 APIs 只能工作于屏幕上可见的 view,另外,依赖于可见的元素数量,可能会有很多的 views 需要进行正确的跟踪并为其制作动画。但另一方面,这种设计又具有一个明显的优势,那就是它可以为所有类型的 UICollectionViewLayout
组合所使用。这样一个系统的实现就留给读者们去进行练习吧。
在附带的演示项目中我们用另一种途径进行了实现,它依赖于一些 UICollectionViewFlowLayout
的巧合。
基本的想法是,因为源 collection view 和目标 collection view 都拥有有效的 flow layouts,因此源 layout 的布局属性正好可以用作目标 collection view 的布局中的初始布局属性,以此驱动转场动画。一旦正确建立,就算对于那些一开始在屏幕上不可见的元素,collection view 的机制都将为我们追踪它们并进行动画。下面是我们的动画控制器中的 animateTransition:
的核心代码:
CGRect initialRect = [inView.window convertRect:_fromCollectionView.frame fromView:_fromCollectionView.superview];
CGRect finalRect = [transitionContext finalFrameForViewController:toVC];
UICollectionViewFlowLayout *toLayout = (UICollectionViewFlowLayout*) _toCollectionView.collectionViewLayout;
UICollectionViewFlowLayout *currentLayout = (UICollectionViewFlowLayout*) _fromCollectionView.collectionViewLayout;
//制作原来布局的拷贝
UICollectionViewFlowLayout *currentLayoutCopy = [[UICollectionViewFlowLayout alloc] init];
currentLayoutCopy.itemSize = currentLayout.itemSize;
currentLayoutCopy.sectionInset = currentLayout.sectionInset;
currentLayoutCopy.minimumLineSpacing = currentLayout.minimumLineSpacing;
currentLayoutCopy.minimumInteritemSpacing = currentLayout.minimumInteritemSpacing;
currentLayoutCopy.scrollDirection = currentLayout.scrollDirection;
//将拷贝赋值给源 collection view
[self.fromCollectionView setCollectionViewLayout:currentLayoutCopy animated:NO];
UIEdgeInsets contentInset = _toCollectionView.contentInset;
CGFloat oldBottomInset = contentInset.bottom;
//强制在目标 collection view 中设定一个很大的 bottom inset
contentInset.bottom = CGRectGetHeight(finalRect)-(toLayout.itemSize.height+toLayout.sectionInset.bottom+toLayout.sectionInset.top);
self.toCollectionView.contentInset = contentInset;
//将源布局设置给目标 collection view
[self.toCollectionView setCollectionViewLayout:currentLayout animated:NO];
toView.frame = initialRect;
[inView insertSubview:toView aboveSubview:fromView];
[UIView
animateWithDuration:[self transitionDuration:transitionContext]
delay:0
options:UIViewAnimationOptionBeginFromCurrentState
animations:^{
//使用最终 frame 制作动画
toView.frame = finalRect;
//在 performUpdates 中设定最终的布局
[_toCollectionView
performBatchUpdates:^{
[_toCollectionView setCollectionViewLayout:toLayout animated:NO];
}
completion:^(BOOL finished) {
_toCollectionView.contentInset = UIEdgeInsetsMake(contentInset.top,
contentInset.left,
oldBottomInset,
contentInset.right);
}];
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
[transitionContext completeTransition:YES];
}];
首先,动画控制器确保目标 collection view 以与原来的 collection view 完全相同的框架和布局作为开始。接着,它将源 collection view 的布局设定给目标 collection view,以确保其不会失效。与此同时,该布局已经复制到另一个新的布局对象中,而这个布局对象则是为防止在导航回原始视图控制器时出现奇怪的布局 bug。我们还会强制在目标 collection view 的底部设定一个很大的 content inset,来确保布局在动画的初始位置时保持在一行上。观察日志的话,你会发现由于元素的尺寸加上 inset 的尺寸会比 collection view 的非滚动维度要大,因此 collection view 会在控制台警告。在这样的情况下,collection view 的行为是没有定义的,我们也只是使用这样一个不稳定的状态来作为我们转换动画的初始状态。最后,复杂的动画 block 将展现它的魅力,首先将目标 collection view 的框架设定到最终位置,然后在 performBatchUpdates:completion: 的 update block 中执行一个无动画的布局来改变至最终布局,紧随其后便是在 completion block 中将 content insets 重置为原始值。
小结
我们讨论了两种可以在 collection view 之间实现布局转场的途径。一种使用了内置的 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions,看起来令人印象深刻并且极其容易实现,缺点就是可以使用的范围较为局限。由于 useLayoutToLayoutNavigationTransitions 在一些案例中不能使用,想驱动自定义的过渡动画的话,就需要一个自定义的 animator。这篇文章中,我们看到了如何实现这样一个 animator,然而,由于你的应用程序大概肯定会需要在两个和本例完全不同的 view 结构中实现完全不同的动画,所以正如此例中做的那样,不要吝于尝试不同的方法来探究其是否能够工作。