一、简介
ConstraintLayout是一个ViewGroup,它允许您以一种灵活的方式定位和调整小部件的大小。借鉴于iOS中的约束,也是Relative的加强版。
android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout在兼容库中,支持Android API 9也就是Android2.3及以上系统版本,拖拽操作进行可视化布局需要在Android Studio 2.2 及以上使用进行。
ConstraintLayout拥有一个完全扁平的层次结构,有效解决了布局嵌套过多的问题,性能更优,速度更快。
关于拖拽式操作可视化布局,可以学习郭霖的这篇文章,我还是习惯代码布局,下面详细介绍:
二、使用
1. 添加依赖
首先需要增加依赖,新版的Android studio已经默认帮助我们添加依赖,并且,我们新建布局文件默认就是使用ConstraintLayout布局
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.1.3'
2. 相对定位(Relative positioning)
可用的约束:
// 约束自己的左边,和某个view的左边对齐
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf
// 基线对齐
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf
可以看出,这些属性形式都一样,都约束一个View的某一边,相对于另一个view的某一边,对齐。
start、end:
在AndroidManifest.xml中的<application>标签下,将属性android:supportsRtl="true",则应用支持从右到左布局,会根据语言文字的书写方式是从左到右还是从右到左,决定start和end,从左到右,则start是左,end是右;从右到左,则start是右,end是左
3. Margin
// 设置自己开始位置的外边距
android:layout_marginStart
android:layout_marginEnd
android:layout_marginLeft
android:layout_marginTop
android:layout_marginRight
android:layout_marginBottom
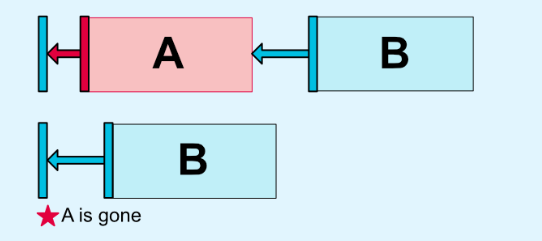
如果要使margin生效,需要设置对应边的约束。但如果宽为match_parent,则相当于有了左右(left、right、start、end)两边的约束,左右都和父布局(constraintLayout)对齐,这是就不用再显示的设置两个边的约束了。 以此类推,高也是一样。
4. goneMargin
app:layout_goneMarginStart
app:layout_goneMarginEnd
app:layout_goneMarginLeft
app:layout_goneMarginTop
app:layout_goneMarginRight
app:layout_goneMarginBottom
当用来约束自身的那个相对view的visible属性为gone时,指定margin值,和上面的margin属性可以同时使用,不冲突,一个是正常的margin,一个是目标view为gone时的margin。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="java"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:visibility="gone"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="android"
android:layout_marginLeft="100dp"
app:layout_goneMarginLeft="50dp"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/button1"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
以上,当button1正常显示时,button2左边距离button1为100dp,当button1为gone时,button2左边距离button1为50dp。
5. 居中定位和偏离率 (Centering positioning and bias)
居中定位:
用我自己的话描述就是:指定好想要居中的方向(垂直、水平)所在的两个边(上下、左右)的约束,在自身的宽高没有撑满指定的约束的宽高,就能实现居中定位,例如:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ……>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="world"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
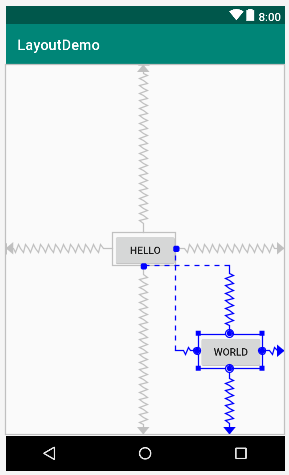
如上,button3就能实现在屏幕的垂直、水平方向都居中的效果,button4则能实现在右下角那块区域的居中效果。
bias
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias
我根据翻译,就叫它偏离率吧。和居中定位配合使用,居中是居中方向两边都是剩余50%的长度,而bias就是不想为50%指定偏离率的属性,可以更好的适应屏幕。
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.3"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.3"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
6. 百分比 (Percent dimension)
三步走:
- 需要设置百分比的一边(宽或高)设置为0dp
-
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="percent"orapp:layout_constraintHeight_default="percent", 1.1-beta1 和 1.1-beta2,需要设置这两个属性,后面就不用了 -
layout_constraintWidth_percentorlayout_constraintHeight_percent attributes设置浮点值在 0 ~ 1之间
// 使用的1.1.3版本
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ……>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="java"
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent="0.6"
app:layout_constraintHeight_percent="0.3"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
如此设置,则该按钮则相对于父布局ConstraintLayout,宽为父布局的0.6,高为父布局的0.3;但是我试验中发现,至少有一个约束,否则不显示。
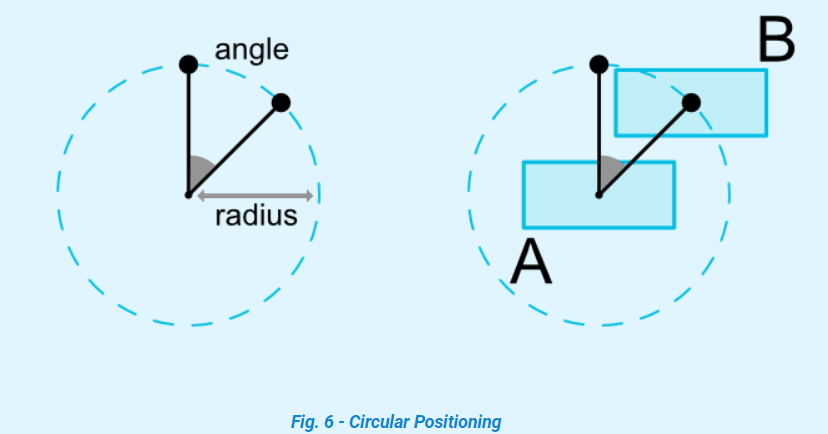
7. 圆形定位 (Circular positioning)
// 指定相对的view
app:layout_constraintCircle
// 指定和相对view中心点的距离
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius
// 指定在相对view一圈360度的哪个角度
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="java"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="0"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="android"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="90"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="world"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="180"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="ios"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="270"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>

8. 宽高比 (Ratio)
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio
这个属性,我理解成宽高比,该属性生效的条件是至少宽或高其中一个属性为 0dp,它的属性值设置为下面三种形式:
-
宽度:高度
例:3:1 ,宽度是高度的三倍 -
宽高比,浮点值。
例:0.5,宽度是高度的三分之一 -
宽或高,宽度:高度在第一种形式的前面加上H或W,用,分隔,字母大小写没限制,需注意的:1. 使用英文符号,2. 不要使用H,0.5这种和上面第二种形式结合的,不是预期效果。
例:H,1:2 ,宽度由系统匹配约束条件计算出值,而高度根据宽度和宽高比得出值
第三种形式有点怪,自己测试了很久,没找出一个合适的规律来,找到一篇博文的评论,非常好,整理如下:
w或h,是指:另一条边通过其他约束获取大小,w或h根据 w:h=ratio 来计算大小。
如果可以通过ratio计算未知边大小,比如,w=100dp,h=0dp,设置 "h,2:1" ,w值100,h通过ratio计算 w:h=2:1 h=w/2=50dp。
如果这个ratio计算无法实现,比如, w=100dp,h=0dp 设置 w,2:1, w已经设置为
固定值,无法通过先获取h,再通过ratio来计算w,这时就通过 h:w=2:1来获取未知的边h的值,h=2w=200dp。 同理,w=0dp,h=100dp设置 h,2:1, h已经设置为固定值,不能通过ratio计算h值,这样 h:w=2:1 w=h/2=50dp。再同理,w=0dp,h=0dp,设置h,2:1,但是w,水平方向没有设置约束条件(系统无法计算宽度,也就无法通过ratio计算h),而设置了垂直方向的约束条件系统可以计算出高度为200dp,h:w=2:1,w = h/2 = 100dp。
一句话,能计算,就按 w:h=ratio 计算未知边;冲突不能计算,就按 h:w=ratio 计算未知边
9. 链 (Chains)

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="java"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@id/button2"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="spread"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="android"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@id/button3"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/button1"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/button2"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
参照代码和图可知,在垂直或水平方向上,两个view双向连接,互相约束,即视为一个链。在链的水平位置最左边或在垂直方向最上边的view被视为链的头。
当在链的第一个元素(head)上设置属性layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle或layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle时,链的行为将根据指定的样式更改(默认是CHAIN_SPREAD)。
可设置属性:
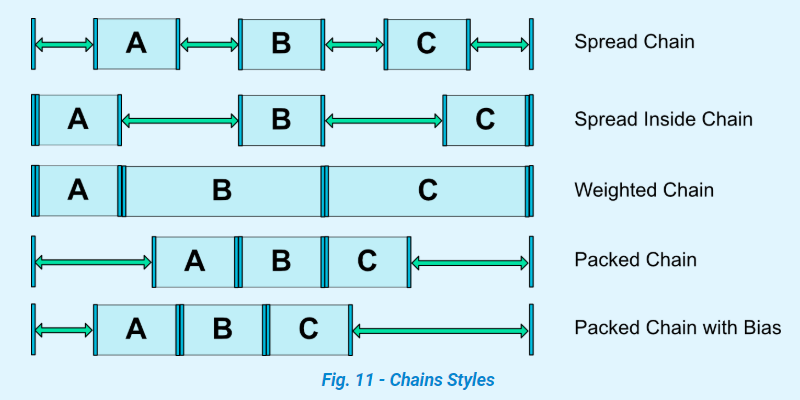
- spread :默认,除去margin,剩余空间(不包含已设置的margin)平均分配到每个view的两边
- spread_inside:类似,但是链的两端不分配剩余空间
- Weighted chain:不是属性,而是当设置为上面两个属性时,链中的view如果宽度为0(垂直链则是高度为0),则这些view平分剩余空间作为自己的宽高。
layout_constraintHorizontal_weight和layout_constraintVertical_weight属性将控制如何使用MATCH_CONSTRAINT在元素之间分配空间。例如其中有两个view的宽或高为0,第一个元素使用权重2,第二个元素使用权重1,第一个元素占用的空间将是第二个元素占用的空间的两倍。 - packed:链的元素会被打包在一起居中显示。
- Packed Chain with Bias:不是属性,而是设置为packed时,水平或垂直bias属性将影响包装元素的位置。
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_biasapp:layout_constraintVertical_bias就是这两个属性,也是在链的head上设置。
10. 辅助布局
只能在ConstraintLayout中使用:
1. Guideline
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<android.support.constraint.Guideline
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/guideline"
app:layout_constraintGuide_begin="100dp"
android:orientation="vertical"/>
<Button
android:text="Button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="@+id/guideline"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
参考线,只是辅助布局,并不会在界面显示出来,默认visible=gone
方向通过android:orientation控制,属性为vertical或horizontal
宽高就默认wrap_cotent就行,设置其他也无效
位置通过app:layout_constraintGuide_begin距离开始位置 layout_constraintGuide_end距离结束位置 layout_constraintGuide_percent距离开始位置百分比,浮点数,如0.5来设置
2. Barrier
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="java"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/place"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="androidddddddd"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/button1"
/>
<android.support.constraint.Barrier
android:id="@+id/barrier"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:barrierDirection="right"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="button1,button2"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="hello"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/barrier"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
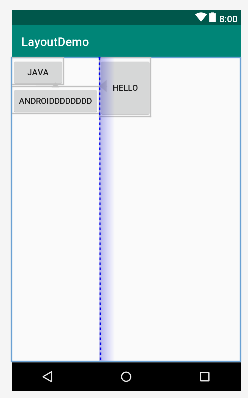
屏障,其实也是个参考线,宽高无效,实际页面不显示。
使用目的如上,我们希望button3在button1和button2的右边,但是,正常情况,我们的button3的左边约束只能指定一个view,button1或button2,但是button1和button2是动态的,如果指定了button1,button2比较长就会被button3覆盖,反之也是,所以就有了barrier,它可以指定多个view,然后形成一条参考线,我们再以这条参考线相对布局。
重要属性:
app:barrierDirection
left、right、top、bottom、start、end
在指定的view集合的某一边形成参考线app:constraint_referenced_ids
指定多个view的id,以,分隔
3. Group
<android.support.constraint.Group
android:id="@+id/group"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="visible"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="button4,button9" />
同时控制多个view的显示和隐藏,app:constraint_referenced_ids控制多个view的id,用,分割;android:visibility控制显示隐藏。
本身不会显示,不占用空间,设置其他宽高也无效。
多个Group可同时控制一个view,以Group在xml中布局顺序决定最终的显示隐藏。
4. Placeholder
<android.support.constraint.Placeholder
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
app:content="@id/button2"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
占位,当设置content时,contentid所代表的view就会消失不见,而在Placeholder中显示,此时Placeholder的宽高设置无效,最终的宽高是contentid所代表的view的宽高。也可以通过代码setContentId(int id)设置。
还可以通过setEmptyVisibility(int visibility)设置Placeholder为空时的显示隐藏,设置为Gone,宽高无效,Placeholder仅是一个点;设置为Visible或Invisible则为设置的宽高,需要根据布局需要设置,这会影响布局。
二、其他六大布局
相信我,只要你上手ConstraintLayout,你将会很少再想去用其他布局,当然特别简单的除外。所以,就不去总结了,布局也都很简单,关键在于多上手练习!附上菜鸟教程的各个布局的教程,感觉这些就够用了:(感谢作者!)
- LinearLayout(线性布局)
- RelativeLayout(相对布局)
- TableLayout(表格布局)
- FrameLayout(帧布局)
- GridLayout(网格布局)
- AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局)
个人总结,水平有限,如果有错误,希望大家能给留言指正!如果对您有所帮助,可以帮忙点个赞!如果转载,希望可以留言告知并在显著位置保留草帽团长的署名和标明文章出处!最后,非常感谢您的阅读!