使用tensorflow
陆陆续续看深度学习也有几天了,基本上还是云里雾里的状态,主要还是数学不好以及一些概念不清楚。选择tensorflow的原因很简单,Google官方以及使用的人还是蛮多的,所以就先从这个入手。用什么工具并不重要,主要还是想学习一下一些思想。
tensorflow的官方文档还是写的很完善的,当然其中的识别数字的案例还是很有名的,有兴趣的可以都看看。
简单案例
我个人感觉,像我这样的初学者一下子看各种案例就会晕头转向,简单的案例还是能够帮助我们更好的去学习这门已经火过3次却2次跌入谷底的技术。
tensorflow提供了一套可以利用cpu和gpu的算法,同时也提供了一套可以展现的dashboard,这一切都可以在代码中进行实现。先看这个简单的代码吧,详细的我全部写在注释里。
# coding:utf-8
# 调用tensorflow
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 这里生成了100对数字,作为整个神经网络的input
x_data = np.random.rand(100).astype("float32")
# 使用with,让我们的数据以节点的方式落在tensorflow的报告上。
with tf.name_scope('y_data'):
y_data = x_data * 2.5 + 0.8 #权重2.5,偏移设置2.5
tf.histogram_summary("method_demo"+"/y_data",y_data) #可视化观看变量y_data
# 指定W和b变量的取值范围,随机在[-200,200]
with tf.name_scope('W'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1], -200.0, 200.0))
tf.histogram_summary("method_demo"+"/W",W) #可视化观看变量
# 指定偏移值b,同时shape等于1
with tf.name_scope('b'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
tf.histogram_summary("method_demo"+"/b",b) #可视化观看变量
with tf.name_scope('y'):
y = W * x_data + b #sigmoid神经元
tf.histogram_summary("method_demo"+"/y",y) #可视化观看变量
# 最小化均方
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data))
tf.histogram_summary("method_demo"+"/loss",loss) #可视化观看变量
tf.scalar_summary("method_demo"+'loss',loss) #可视化观看常量
# 定义学习率,我们先使用0.7来看看效果
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.7)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# 初始化TensorFlow参数
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# 运行数据流图
sess = tf.Session()
#合并到Summary中
merged = tf.merge_all_summaries()
#选定可视化存储目录
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter(LOG_PATH,sess.graph)
sess.run(init)
# 开始计算
for step in xrange(500):
sess.run(train)
if step % 5 == 0:
print(step, "W:",sess.run(W),"b:", sess.run(b))
result = sess.run(merged) #merged也是需要run的
writer.add_summary(result,step) #result是summary类型的
运行之后可以在我们设置的目录下得到events.out.tfevents.xxxxx.yyyy.local这样一个记录文件,这个记录文件我们可以使用tensorboard --logdir=命令在本地浏览器中打开我们的报告。在我们查看之前我们先来说下这段脚本的目的,目标就是经过训练之后,我们的权重和偏移值能够无限接近甚至等于我们开始预期的那个值。也就是我们说的最小化loss。
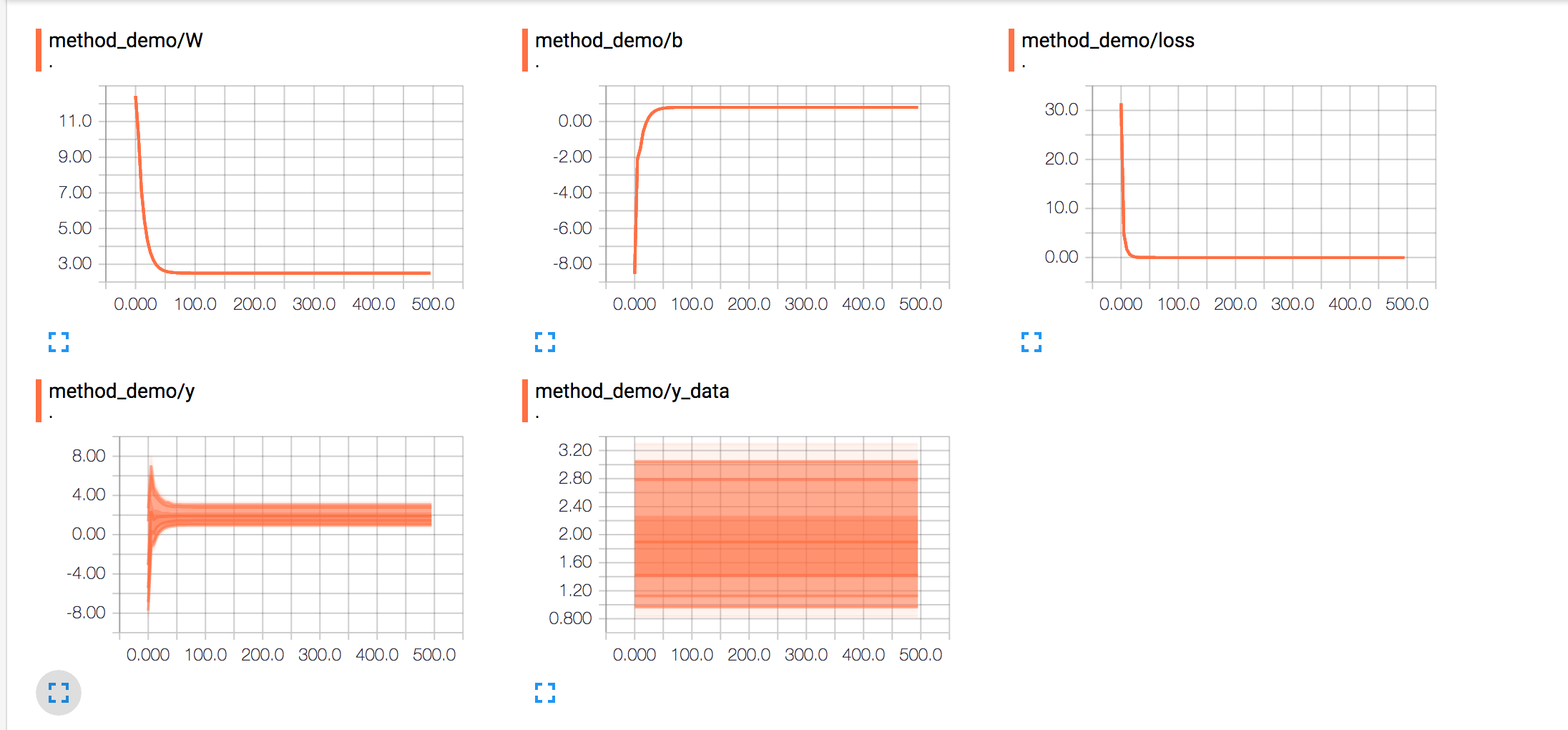
我们可以看到loss的趋势图在无限接近于0
其他的数值我们再一起来看下,权重和偏移值以及我们的实际值都再无限偏向于我们的期望值,也就是代码最早设置的w,b以及y_data
other
既然有了案例,那么需要多折腾试试看。代码中的学习在0.7,我们看下前100次训练的数据。w大概在50次左右就已经很接近我们的期望值了,而b大概在100次左右。
(0, 'W:', array([ 28.7924614], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-26.07459641], dtype=float32))
(5, 'W:', array([ 22.93203735], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-6.60854244], dtype=float32))
(10, 'W:', array([ 14.21786118], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-5.31221294], dtype=float32))
(15, 'W:', array([ 9.79547119], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-2.6562953], dtype=float32))
(20, 'W:', array([ 6.93433905], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-1.36106539], dtype=float32))
(25, 'W:', array([ 5.21388531], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-0.51195335], dtype=float32))
(30, 'W:', array([ 4.15765142], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-0.00321657], dtype=float32))
(35, 'W:', array([ 3.51307726], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.30944157], dtype=float32))
(40, 'W:', array([ 3.11904287], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.50018537], dtype=float32))
(45, 'W:', array([ 2.87828541], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.61679912], dtype=float32))
(50, 'W:', array([ 2.73115993], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.6880492], dtype=float32))
(55, 'W:', array([ 2.64125586], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.73159003], dtype=float32))
(60, 'W:', array([ 2.58631778], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.75819641], dtype=float32))
(65, 'W:', array([ 2.55274653], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.77445489], dtype=float32))
(70, 'W:', array([ 2.53223205], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.78439009], dtype=float32))
(75, 'W:', array([ 2.51969624], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.79046112], dtype=float32))
(80, 'W:', array([ 2.51203585], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.79417104], dtype=float32))
(85, 'W:', array([ 2.50735474], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.79643804], dtype=float32))
(90, 'W:', array([ 2.50449443], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.79782349], dtype=float32))
(95, 'W:', array([ 2.50274634], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.79866987], dtype=float32))
(100, 'W:', array([ 2.50167823], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([ 0.79918718], dtype=float32))
学习速率在0-1中取值,数值越小就好像每次学习迈出的步子越小,每次训练的跨度不会很大。而0.9的话则相反。改成0.1之后我们训练的次数就会变多,甚至在训练结束我们都得不到想要的值
(0, 'W:', array([ 126.14640045], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-12.36228561], dtype=float32))
(5, 'W:', array([ 104.47080231], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-39.09550095], dtype=float32))
(10, 'W:', array([ 94.78070068], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-43.2287178], dtype=float32))
(15, 'W:', array([ 88.2450943], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-42.08102036], dtype=float32))
(20, 'W:', array([ 82.72779846], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-39.79907227], dtype=float32))
(25, 'W:', array([ 77.70004272], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-37.3695755], dtype=float32))
(30, 'W:', array([ 73.01972198], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-35.02152634], dtype=float32))
(35, 'W:', array([ 68.63846588], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-32.80261612], dtype=float32))
(40, 'W:', array([ 64.53126526], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-30.71748161], dtype=float32))
(45, 'W:', array([ 60.67957306], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-28.76085472], dtype=float32))
(50, 'W:', array([ 57.06715012], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-26.92548561], dtype=float32))
(55, 'W:', array([ 53.67905426], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-25.20401955], dtype=float32))
(60, 'W:', array([ 50.50133133], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-23.58942795], dtype=float32))
(65, 'W:', array([ 47.52091217], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-22.07508087], dtype=float32))
(70, 'W:', array([ 44.72555161], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-20.65476227], dtype=float32))
(75, 'W:', array([ 42.10375977], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-19.32262993], dtype=float32))
(80, 'W:', array([ 39.64474487], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-18.07320976], dtype=float32))
(85, 'W:', array([ 37.33841705], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-16.90136719], dtype=float32))
(90, 'W:', array([ 35.17529297], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-15.80228519], dtype=float32))
(95, 'W:', array([ 33.14647675], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-14.77144527], dtype=float32))
(100, 'W:', array([ 31.24362946], dtype=float32), 'b:', array([-13.80461025], dtype=float32))
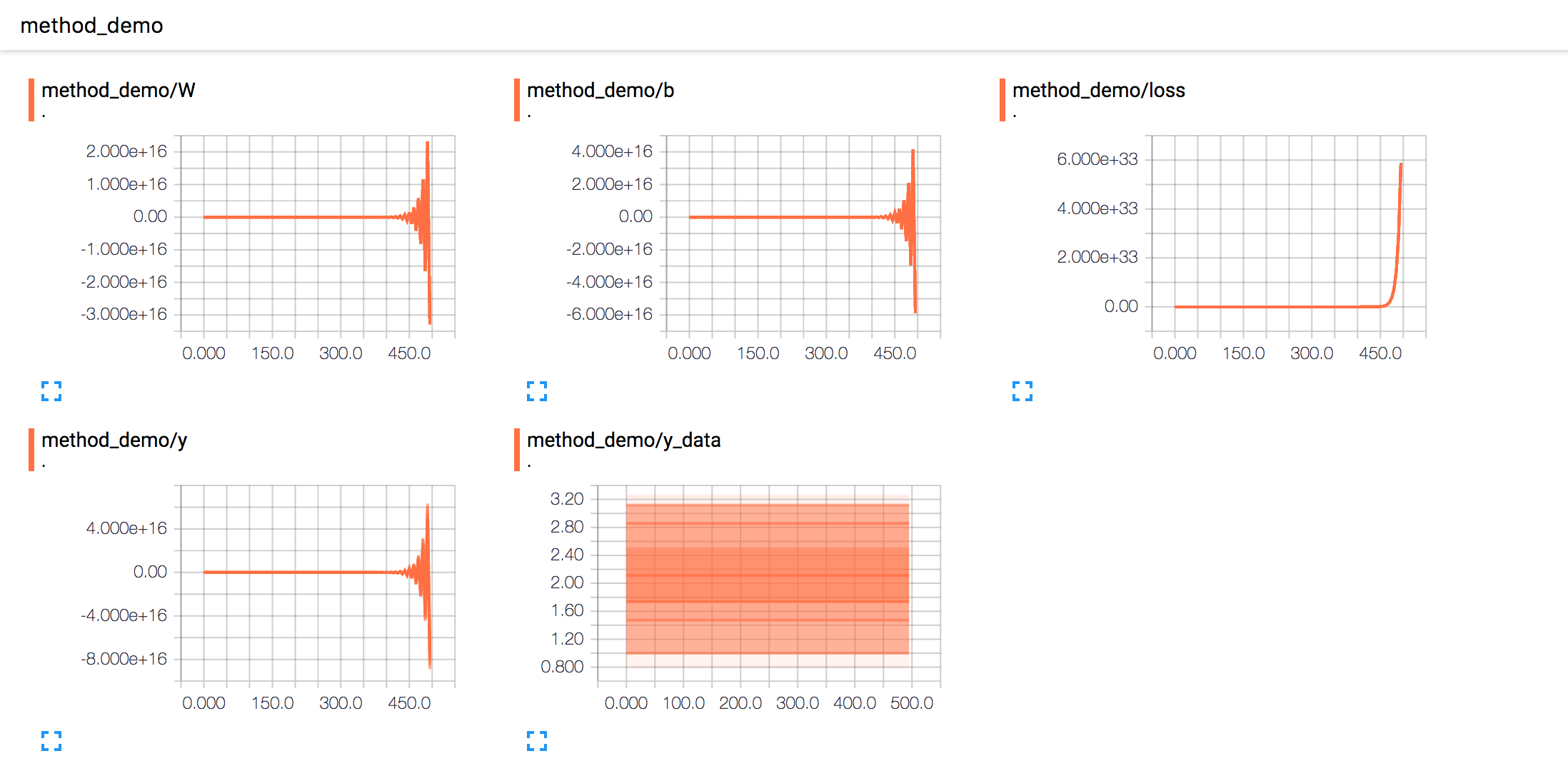
相反如果比较大,偏导数则可能收敛的很慢,甚至发散。比如下面的报告

总结
希望案例能使用够帮助大家更好的使用tensorflow以及了解一些基础的方法。推荐在进行尝试之前阅读gitbook